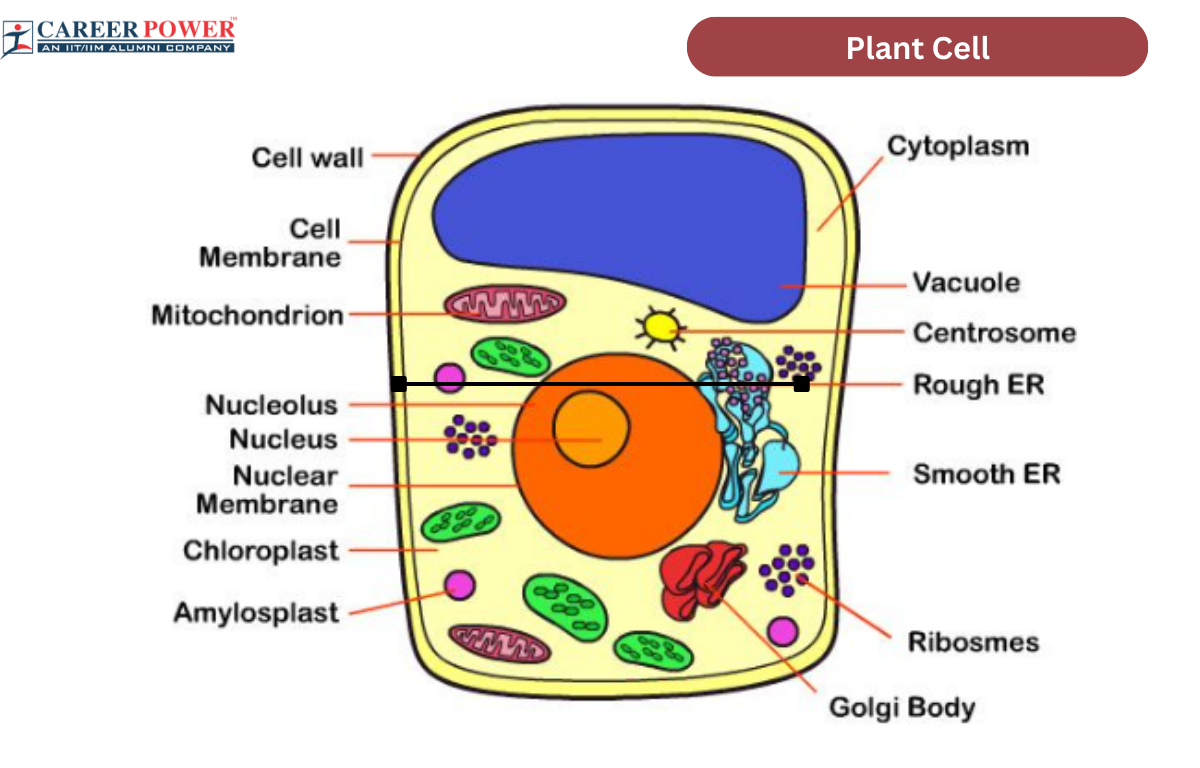
Learning how to create a plant cell diagram is essential for understanding the structure and functions of cells. Follow these steps to create an accurate diagram:
- Gather materials: You will need a blank paper, colored pencils or markers, and a reference image of a plant cell.
- Draw the cell membrane: Start by drawing a large oval shape to represent the outer boundary of the cell.
- Add the cell wall: Draw a thicker line outside the cell membrane to represent the rigid cell wall.
- Include the organelles: Use different shapes and colors to represent the various organelles inside the cell, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts.
- Label the parts: Add labels to each organelle to indicate its name and function.When it comes to understanding the intricate structures of plant cells, a visual representation can be incredibly helpful. Did you know that a plant cell diagram provides a detailed overview of the different organelles and structures within a plant cell? From the nucleus and chloroplasts to the cell wall and vacuole, a plant cell diagram allows us to explore the inner workings of these vital building blocks of life. By studying and learning to create a plant cell diagram, we can gain a deeper understanding of how plants function and adapt to their environments.
Plant cell diagrams have been used for centuries to help scientists and students alike understand the intricate world of plant biology. The first detailed observations of plant cells were made by the renowned botanist, Robert Hooke, in the 17th century. Since then, advancements in microscopic technology have allowed us to delve even further into the complexities of plant cells. Today, plant cell diagrams are not only used in educational settings but also in research laboratories around the world. By studying and analyzing these diagrams, scientists are able to make discoveries that can contribute to advancements in agriculture, medicine, and environmental sustainability.

Source: sciencenotes.org How To Plant Cell Diagram: A Comprehensive Guide
The study of plant cells is crucial for understanding the biological processes that occur within plants. One effective way to analyze plant cells is by creating a plant cell diagram. This diagram provides a visual representation of the various components and structures found within a plant cell. In this article, we will explore the process of creating a plant cell diagram, including the essential components, tools required, and the step-by-step procedure. By the end of this guide, you will have all the knowledge you need to create an accurate and informative plant cell diagram.
Before we dive into the details of how to create a plant cell diagram, let’s briefly discuss the importance of understanding plant cells and their structures. Plant cells are the basic building blocks of plants and are responsible for carrying out essential functions such as photosynthesis, nutrient absorption, and cell division. By studying the structures and components of plant cells, scientists can gain insights into how plants function and develop strategies to enhance plant growth and productivity.
To begin creating a plant cell diagram, you will need a few essential tools. These include:
- Pencil or pen
- Plain white paper or a sketchbook
- Ruler
- Coloring materials such as colored pencils or markers
These tools will help you draw and label the different components of a plant cell accurately. Once you have gathered these materials, you can proceed with the step-by-step process of creating a plant cell diagram.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Plant Cell Diagram
Step 1: Draw the Outline of the Plant Cell
The first step in creating a plant cell diagram is to draw the outline of the cell. Begin by drawing a rectangular shape to represent the cell membrane. This outer boundary encloses all the internal components of the plant cell. Use a ruler to create straight lines and ensure accuracy in your diagram. Leave some space around the edges of the rectangle to label the different parts of the plant cell.
Once you have drawn the cell membrane, add a smaller rectangle in the center to represent the nucleus. The nucleus is a vital organelle that contains the plant cell’s genetic material and controls the cell’s activities. Be sure to position the nucleus within the cell membrane accurately.
Fun fact: The nucleus is often referred to as the “brain” of the cell due to its role in controlling cell functions.
Next, draw several smaller circles within the cell membrane to represent other essential organelles such as mitochondria, vacuoles, and chloroplasts. These organelles play critical roles in various cellular processes.
Finally, add the cell wall outside the cell membrane. The cell wall provides structural support and protection to the plant cell.

Step 2: Label the Components of the Plant Cell
Once you have drawn the outline of the plant cell, the next step is to label the different components. Start with the nucleus and label it accordingly. You can use a small arrow or underline to connect the label to the nucleus. This will make it clear which part of the diagram you are referring to.
Continue labeling the other organelles within the cell, such as mitochondria, vacuoles, and chloroplasts. Use clear and concise labels to ensure understanding.
In addition to the organelles, you should also label the cell membrane and cell wall. These structures play essential roles in maintaining the integrity of the plant cell.
If you are feeling creative, you can use colored pencils or markers to color in the different parts of the plant cell diagram. This will make your diagram visually appealing and easier to understand.
Step 3: Add Additional Details and Annotations
Once you have labeled the components of the plant cell, you can add additional details and annotations to enhance the diagram’s educational value. This could include providing brief explanations of the function of each organelle or highlighting any unique features of plant cells.
Adding annotations not only makes your diagram more informative but also helps you reinforce your understanding of plant cell structures and functions.
Remember to use clear and concise language when writing annotations. Use bullet points or numbered lists to organize the information effectively.
Conclusion
Creating a plant cell diagram is a valuable exercise that allows you to visualize and understand the various components and structures of a plant cell. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this article, you can create an accurate and informative plant cell diagram. Remember to use the proper tools, draw clear outlines, label the components, and add annotations to enhance the educational value. Whether you are a student studying biology or a plant enthusiast, a plant cell diagram is an excellent tool for learning and appreciation.
Further explore the fascinating world of plant cells and their structures by visiting the Plant Cell Biology website. This comprehensive resource provides in-depth information about plant cells, their functions, and ongoing research in the field.

Source: Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about planting a cell diagram.
1. How do I create a plant cell diagram?
To create a plant cell diagram, you will need a blank piece of paper, colored pencils or markers, and a reference image or diagram of a plant cell. Start by drawing an oval shape in the center of the paper to represent the cell. Then, add in the various organelles of the plant cell, such as the nucleus, cell wall, chloroplasts, and vacuole. Use the colored pencils or markers to differentiate the different parts and add labels as necessary. Remember to refer to your reference image or diagram to ensure accuracy.
If you are creating the diagram for educational purposes, consider adding additional details or annotations to highlight the functions of each organelle. This can help enhance understanding and make the diagram more informative.
2. What is the purpose of a plant cell diagram?
A plant cell diagram serves as a visual representation of the different components and structures within a plant cell. It helps in understanding the organization and function of various organelles within the cell. By studying a plant cell diagram, students and researchers can identify and learn about the different parts of a plant cell, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and vacuole, and understand how they work together to carry out essential cellular processes like photosynthesis, respiration, and protein synthesis.
In educational settings, a plant cell diagram is often used as a teaching tool to introduce students to the basics of cell biology and plant anatomy. It provides a visual aid for learning and allows students to visualize the structures and functions of a plant cell in a more interactive and engaging way.
3. Can I use digital tools to create a plant cell diagram?
Absolutely! Using digital tools to create a plant cell diagram can be a convenient and efficient method, especially for those who prefer a more precise and polished result. There are various software and online platforms available that offer pre-designed templates and tools specifically designed for creating scientific diagrams, including plant cell diagrams.
You can use graphic design software like Adobe Illustrator or PowerPoint, or try online applications like Lucidchart or Canva. These tools allow you to easily draw each organelle, customize their appearance, add labels, and even create interactive diagrams that can be shared and accessed digitally. Additionally, creating a digital plant cell diagram offers the flexibility to edit and modify the diagram as needed.
4. Are there any websites or resources that provide pre-made plant cell diagram templates?
Yes, there are several websites and resources that offer pre-made plant cell diagram templates that you can use as a starting point or reference. These templates typically include the basic structure of a plant cell, allowing you to focus on adding details and labels to customize the diagram.
Some popular websites that provide free plant cell diagram templates include Canva, Lucidchart, and Pinterest. You can also find educational websites and biology textbooks that offer printable diagrams for educational purposes. When using pre-made templates, make sure to credit the source if required and modify the diagram to suit your specific needs.
5. How can I make my plant cell diagram more visually appealing?
To make your plant cell diagram more visually appealing, consider the following tips:
– Use vibrant and contrasting colors to differentiate the different organelles and make them visually striking.
– Pay attention to the layout and spacing of the organelles to create a balanced and aesthetically pleasing composition.
– Add shading or gradients to create depth and dimension in the diagram.
– Incorporate illustrations or icons that represent the functions of each organelle, making the diagram more informative and engaging.
– Consider using digital tools or software that offer advanced design features, such as various shapes, textures, and effects, to enhance the visual appeal of the diagram.
To create a plant cell diagram, start with a round shape for the cell. Then, draw a thick outer wall called the cell wall. Inside the cell, add a smaller circle for the nucleus, which is like the cell’s control center.
Next, draw oval shapes for the chloroplasts, which help the cell make food through photosynthesis. Add small dots for the mitochondria, which produce energy for the cell. Finally, include smaller circles for the vacuoles, which store water and nutrients. And that’s it—a simple and easy plant cell diagram!